Influenza A virus subtype H5N1
From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
(Redirected from H5N1)
 |
| Influenza (Flu) |
|---|
 |
| Types |
|
| Vaccines |
| Treatment |
| Pandemics |
| Outbreaks |
| See also |
According to the FAO Avian Influenza Disease Emergency Situation Update, H5N1 pathogenicity is continuing to gradually rise in endemic areas, but the avian influenza disease situation in farmed birds is being held in check by vaccination. Eleven outbreaks of H5N1 were reported worldwide in June 2008 in five countries (China, Egypt, Indonesia, Pakistan and Vietnam) compared to 65 outbreaks in June 2006 and 55 in June 2007. The "global HPAI situation can be said to have improved markedly in the first half of 2008 [but] cases of HPAI are still underestimated and underreported in many countries because of limitations in country disease surveillance systems".[3] On October 10, 2011 the WHO announced a total of 566 human cases which resulted in the deaths of 332 people since 2003.[4]
A filtered and purified influenza A vaccine for humans is being developed, and many countries have recommended it be stockpiled so, if an avian influenza pandemic starts jumping to humans, the vaccine can quickly be administered to avoid loss of life. Avian influenza is sometimes called avian flu, and commonly bird flu.
A novel, highly contagious strain of H5N1 was created by Ron Fouchier of the Erasmus Medical Centre in Rotterdam, the Netherlands, who first presented his work to the public at an influenza conference in Malta in September 2011.[5] Five mutations were introduced into the H5N1 genome, and the virus was then bred by passing it from the noses of infected ferrets to the noses of uninfected ones, which was repeated 10 times.[6] Fouchier described the result as "probably one of the most dangerous viruses you can make".[7]
Contents[hide] |
[edit] Overview
HPAI A(H5N1) is considered an avian disease, although there is some evidence of limited human-to-human transmission of the virus.[8] A risk factor for contracting the virus is handling of infected poultry, but transmission of the virus from infected birds to humans is inefficient.[9] Still, around 60% of humans known to have been infected with the current Asian strain of HPAI A(H5N1) have died from it, and H5N1 may mutate or reassort into a strain capable of efficient human-to-human transmission. In 2003, world-renowned virologist Robert G. Webster published an article titled "The world is teetering on the edge of a pandemic that could kill a large fraction of the human population" in American Scientist. He called for adequate resources to fight what he sees as a major world threat to possibly billions of lives.[10] On September 29, 2005, David Nabarro, the newly appointed Senior United Nations System Coordinator for Avian and Human Influenza, warned the world that an outbreak of avian influenza could kill anywhere between 5 million and 150 million people.[11] Experts have identified key events (creating new clades, infecting new species, spreading to new areas) marking the progression of an avian flu virus towards becoming pandemic, and many of those key events have occurred more rapidly than expected.Due to the high lethality and virulence of HPAI A(H5N1), its endemic presence, its increasingly large host reservoir, and its significant ongoing mutations, the H5N1 virus is the world's largest current pandemic threat, and billions of dollars are being spent researching H5N1 and preparing for a potential influenza pandemic.[12] At least 12 companies and 17 governments are developing prepandemic influenza vaccines in 28 different clinical trials that, if successful, could turn a deadly pandemic infection into a nondeadly one. Full-scale production of a vaccine that could prevent any illness at all from the strain would require at least three months after the virus's emergence to begin, but it is hoped that vaccine production could increase until one billion doses were produced by one year after the initial identification of the virus.[13]
H5N1 may cause more than one influenza pandemic, as it is expected to continue mutating in birds regardless of whether humans develop herd immunity to a future pandemic strain.[14] Influenza pandemics from its genetic offspring may include influenza A virus subtypes other than H5N1.[15] While genetic analysis of the H5N1 virus shows that influenza pandemics from its genetic offspring can easily be far more lethal than the Spanish flu pandemic,[16] planning for a future influenza pandemic is based on what can be done and there is no higher Pandemic Severity Index level than a Category 5 pandemic which, roughly speaking, is any pandemic as bad as the Spanish flu or worse; and for which all intervention measures are to be used.[17]
[edit] Signs and symptoms
Further information: Influenza
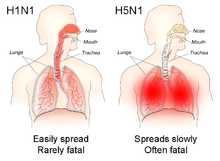
The different sites of infection (shown in red) of seasonal H1N1 versus avian H5N1 influences their lethality and ability to spread.[18]
The reported mortality rate of highly pathogenic H5N1 avian influenza in a human is high; WHO data indicate 60% of cases classified as H5N1 resulted in death. However, there is some evidence the actual mortality rate of avian flu could be much lower, as there may be many people with milder symptoms who do not seek treatment and are not counted.[21][22]
In one case, a boy with H5N1 experienced diarrhea followed rapidly by a coma without developing respiratory or flu-like symptoms.[23] There have been studies of the levels of cytokines in humans infected by the H5N1 flu virus. Of particular concern is elevated levels of tumor necrosis factor-alpha, a protein associated with tissue destruction at sites of infection and increased production of other cytokines. Flu virus-induced increases in the level of cytokines is also associated with flu symptoms, including fever, chills, vomiting and headache. Tissue damage associated with pathogenic flu virus infection can ultimately result in death.[10] The inflammatory cascade triggered by H5N1 has been called a 'cytokine storm' by some, because of what seems to be a positive feedback process of damage to the body resulting from immune system stimulation. H5N1 induces higher levels of cytokines than the more common flu virus types.[24]
[edit] Genetics
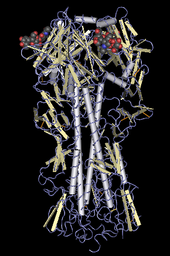
The H in H5N1 stands for "hemagglutinin", as depicted in this molecular model
Further information: Influenzavirus A and H5N1 genetic structure
The first known strain of HPAI A(H5N1) (called A/chicken/Scotland/59) killed two flocks of chickens in Scotland in 1959, but that strain was very different from the current highly pathogenic strain of H5N1. The dominant strain of HPAI A(H5N1) in 2004 evolved from 1999 to 2002 creating the Z genotype.[25] It has also been called "Asian lineage HPAI A(H5N1)".Asian lineage HPAI A(H5N1) is divided into two antigenic clades. "Clade 1 includes human and bird isolates from Vietnam, Thailand, and Cambodia and bird isolates from Laos and Malaysia. Clade 2 viruses were first identified in bird isolates from China, Indonesia, Japan, and South Korea before spreading westward to the Middle East, Europe, and Africa. The clade 2 viruses have been primarily responsible for human H5N1 infections that have occurred during late 2005 and 2006, according to WHO. Genetic analysis has identified six subclades of clade 2, three of which have a distinct geographic distribution and have been implicated in human infections: Map
- Subclade 1, Indonesia
- Subclade 2, Europe, Middle East, and Africa (called EMA)
- Subclade 3, China"[14][26][27]
[edit] Terminology
H5N1 isolates are identified like this actual HPAI A(H5N1) example, A/chicken/Nakorn-Patom/Thailand/CU-K2/04(H5N1):- A stands for the species of influenza (A, B or C).
- chicken is the species the isolate was found in
- Nakorn-Patom/Thailand is the place this specific virus was isolated
- CU-K2 identifies it from other influenza viruses isolated at the same place
- 04 represents the year 2004
- H5 stands for the fifth of several known types of the protein hemagglutinin.
- N1 stands for the first of several known types of the protein neuraminidase.
As with other avian flu viruses, H5N1 has strains called "highly pathogenic" (HP) and "low-pathogenic" (LP). Avian influenza viruses that cause HPAI are highly virulent, and mortality rates in infected flocks often approach 100%. LPAI viruses have negligible virulence, but these viruses can serve as progenitors to HPAI viruses. The current strain of H5N1 responsible for the deaths of birds across the world is an HPAI strain; all other current strains of H5N1, including a North American strain that causes no disease at all in any species, are LPAI strains. All HPAI strains identified to date have involved H5 and H7 subtypes. The distinction concerns pathogenicity in poultry, not humans. Normally, a highly pathogenic avian virus is not highly pathogenic to either humans or nonpoultry birds. This current deadly strain of H5N1 is unusual in being deadly to so many species, including some, like domestic cats, never previously susceptible to any influenza virus.[30]
[edit]

The N in H5N1 stands for "Neuraminidase", the protein depicted in this ribbon diagram.
HA codes for hemagglutinin, an antigenic glycoprotein found on the surface of the influenza viruses and is responsible for binding the virus to the cell that is being infected. NA codes for neuraminidase, an antigenic glycosylated enzyme found on the surface of the influenza viruses. It facilitates the release of progeny viruses from infected cells.[31] The hemagglutinin (HA) and neuraminidase (NA) RNA strands specify the structure of proteins that are most medically relevant as targets for antiviral drugs and antibodies. HA and NA are also used as the basis for the naming of the different subtypes of influenza A viruses. This is where the H and N come from in H5N1.
Influenza A viruses are significant for their potential for disease and death in humans and other animals. Influenza A virus subtypes that have been confirmed in humans, in order of the number of known human pandemic deaths that they have caused, include:
- H1N1, which caused the 1918 flu pandemic ("Spanish flu") and currently is causing seasonal human flu and the 2009 flu pandemic ("swine flu")
- H2N2, which caused "Asian flu"
- H3N2, which caused "Hong Kong flu" and currently causes seasonal human flu
- H5N1, ("bird flu"), which is noted for having a strain (Asian-linage HPAI H5N1) that kills over half the humans it infects, infecting and killing species that were never known to suffer from influenza viruses before (e.g. cats), being unable to be stopped by culling all involved poultry - some think due to being endemic in wild birds, and causing billions of dollars to be spent in flu pandemic preparation and preventiveness
- H7N7, which has unusual zoonotic potential and killed one person
- H1N2, which is currently endemic in humans and pigs and causes seasonal human flu
- H9N2, which has infected three people
- H7N2, which has infected two people
- H7N3, which has infected two people
- H10N7, which has infected two people
[edit] Low pathogenic H5N1
Low pathogenic avian influenza H5N1 (LPAI H5N1) also called "North American" H5N1 commonly occurs in wild birds. In most cases, it causes minor sickness or no noticeable signs of disease in birds. It is not known to affect humans at all. The only concern about it is that it is possible for it to be transmitted to poultry and in poultry mutate into a highly pathogenic strain.- 1975 – LPAI H5N1 was detected in a wild mallard duck and a wild blue goose in Wisconsin.
- 1981 and 1985 – LPAI H5N1 was detected in ducks by the University of Minnesota conducting a sampling procedure in which sentinel ducks were monitored in cages placed in the wild for a short period of time.
- 1983 – LPAI H5N1 was detected in ring-billed gulls in Pennsylvania.
- 1986 - LPAI H5N1 was detected in a wild mallard duck in Ohio.
- 2005 - LPAI H5N1 was detected in ducks in Manitoba, Canada.
- 2008 - LPAI H5N1 was detected in ducks in New Zealand.
- 2009 - LPAI H5N1 was detected in commercial poultry in British Columbia.[32]
[edit] High mutation rate
Influenza viruses have a relatively high mutation rate that is characteristic of RNA viruses. The segmentation of its genome facilitates genetic recombination by segment reassortment in hosts infected with two different influenza viruses at the same time.[34][35] A previously uncontagious strain may then be able to pass between humans, one of several possible paths to a pandemic.The ability of various influenza strains to show species-selectivity is largely due to variation in the hemagglutinin genes. Genetic mutations in the hemagglutinin gene that cause single amino acid substitutions can significantly alter the ability of viral hemagglutinin proteins to bind to receptors on the surface of host cells. Such mutations in avian H5N1 viruses can change virus strains from being inefficient at infecting human cells to being as efficient in causing human infections as more common human influenza virus types.[36] This doesn't mean that one amino acid substitution can cause a pandemic, but it does mean that one amino acid substitution can cause an avian flu virus that is not pathogenic in humans to become pathogenic in humans.
Influenza A virus subtype H3N2 is endemic in pigs in China, and has been detected in pigs in Vietnam, increasing fears of the emergence of new variant strains. The dominant strain of annual flu virus in January 2006 was H3N2, which is now resistant to the standard antiviral drugs amantadine and rimantadine. The possibility of H5N1 and H3N2 exchanging genes through reassortment is a major concern. If a reassortment in H5N1 occurs, it might remain an H5N1 subtype, or it could shift subtypes, as H2N2 did when it evolved into the Hong Kong Flu strain of H3N2.
Both the H2N2 and H3N2 pandemic strains contained avian influenza virus RNA segments. "While the pandemic human influenza viruses of 1957 (H2N2) and 1968 (H3N2) clearly arose through reassortment between human and avian viruses, the influenza virus causing the 'Spanish flu' in 1918 appears to be entirely derived from an avian source".[25]
[edit] Prevention
There are several H5N1 vaccines for several of the avian H5N1 varieties, but the continual mutation of H5N1 renders them of limited use to date: while vaccines can sometimes provide cross-protection against related flu strains, the best protection would be from a vaccine specifically produced for any future pandemic flu virus strain. Dr. Daniel Lucey, co-director of the Biohazardous Threats and Emerging Diseases graduate program at Georgetown University has made this point, "There is no H5N1 pandemic so there can be no pandemic vaccine".[37] However, "pre-pandemic vaccines" have been created; are being refined and tested; and do have some promise both in furthering research and preparedness for the next pandemic.[38][39][40] Vaccine manufacturing companies are being encouraged to increase capacity so that if a pandemic vaccine is needed, facilities will be available for rapid production of large amounts of a vaccine specific to a new pandemic strain.[edit] Public health
| The examples and perspective in this article may not represent a worldwide view of the subject. Please improve this article and discuss the issue on the talk page. (January 2010) |
Further information: Influenza pandemic
"The United States is collaborating closely with eight international organizations, including the World Health Organization (WHO), the Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations (FAO), the World Organization for Animal Health (OIE), and 88 foreign governments to address the situation through planning, greater monitoring, and full transparency in reporting and investigating avian influenza occurrences. The United States and these international partners have led global efforts to encourage countries to heighten surveillance for outbreaks in poultry and significant numbers of deaths in migratory birds and to rapidly introduce containment measures. The U.S. Agency for International Development (USAID) and the U.S. Department of State, the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services (HHS), and Agriculture (USDA) are coordinating future international response measures on behalf of the White House with departments and agencies across the federal government".[41]Together steps are being taken to "minimize the risk of further spread in animal populations", "reduce the risk of human infections", and "further support pandemic planning and preparedness".[41]
Ongoing detailed mutually coordinated onsite surveillance and analysis of human and animal H5N1 avian flu outbreaks are being conducted and reported by the USGS National Wildlife Health Center, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, the World Health Organization, the European Commission, and others.[42]
[edit] Treatment
Further information: Flu research
There is no highly effective treatment for H5N1 flu, but oseltamivir (commercially marketed by Roche as Tamiflu), can sometimes inhibit the influenza virus from spreading inside the user's body. This drug has become a focus for some governments and organizations trying to prepare for a possible H5N1 pandemic.[43] On April 20, 2006, Roche AG announced that a stockpile of three million treatment courses of Tamiflu are waiting at the disposal of the World Health Organization to be used in case of a flu pandemic; separately Roche donated two million courses to the WHO for use in developing nations that may be affected by such a pandemic but lack the ability to purchase large quantities of the drug.[44]However, WHO expert Hassan al-Bushra has said:
- "Even now, we remain unsure about Tamiflu's real effectiveness. As for a vaccine, work cannot start on it until the emergence of a new virus, and we predict it would take six to nine months to develop it. For the moment, we cannot by any means count on a potential vaccine to prevent the spread of a contagious influenza virus, whose various precedents in the past 90 years have been highly pathogenic".[45]
[edit] Epidemiology
Further information: Transmission and infection of H5N1 and Global spread of H5N1
The earliest infections of humans by H5N1 coincided with an epizootic (an epidemic in nonhumans) of H5N1 influenza in Hong Kong's poultry population. This panzootic (a disease affecting animals of many species, especially over a wide area) outbreak was stopped by the killing of the entire domestic poultry population within the territory. However, the disease has continued to spread. On December 21, 2009 the WHO announced a total of 447 cases which resulted in the deaths of 263.[4][edit] Contagiousness
H5N1 is mainly spread by domestic poultry, both through the movements of infected birds and poultry products and through the use of infected poultry manure as fertilizer or feed. Humans with H5N1 have typically caught it from chickens, which were in turn infected by other poultry or waterfowl. Migrating waterfowl (wild ducks, geese and swans) carry H5N1, often without becoming sick.[53][54] Many species of birds and mammals can be infected with HPAI A(H5N1), but the role of animals other than poultry and waterfowl as disease-spreading hosts is unknown.[55]
According to a report by the World Health Organization, H5N1 may be spread indirectly. The report stated that the virus may sometimes stick to surfaces or get kicked up in fertilizer dust to infect people.[56]
[edit] Virulence
H5N1 has mutated into a variety of strains with differing pathogenic profiles, some pathogenic to one species but not others, some pathogenic to multiple species. Each specific known genetic variation is traceable to a virus isolate of a specific case of infection. Through antigenic drift, H5N1 has mutated into dozens of highly pathogenic varieties divided into genetic clades which are known from specific isolates, but all currently belonging to genotype Z of avian influenza virus H5N1, now the dominant genotype.[35][34] H5N1 isolates found in Hong Kong in 1997 and 2001 were not consistently transmitted efficiently among birds and did not cause significant disease in these animals. In 2002 new isolates of H5N1 were appearing within the bird population of Hong Kong. These new isolates caused acute disease, including severe neurological dysfunction and death in ducks. This was the first reported case of lethal influenza virus infection in wild aquatic birds since 1961.[57] Genotype Z emerged in 2002 through reassortment from earlier highly pathogenic genotypes of H5N1[2] that first infected birds in China in 1996, and first infected humans in Hong Kong in 1997.[34][35][58] Genotype Z is endemic in birds in Southeast Asia, has created at least two clades that can infect humans, and is spreading across the globe in bird populations. Mutations are occurring within this genotype that are increasing their pathogenicity.[59] Birds are also able to shed the virus for longer periods of time before their death, increasing the transmissibility of the virus.[edit] Transmission and host range

Influenza A virus, the virus that causes Avian flu. Transmission electron micrograph of negatively stained virus particles in late passage. (Source: Dr. Erskine Palmer, Centers for Disease Control and Prevention Public Health Image Library)
Because migratory birds are among the carriers of the highly pathogenic H5N1 virus, it is spreading to all parts of the world. H5N1 is different from all previously known highly pathogenic avian flu viruses in its ability to be spread by animals other than poultry.
In October 2004, researchers discovered that H5N1 is far more dangerous than was previously believed. Waterfowl were revealed to be directly spreading the highly pathogenic strain of H5N1 to chickens, crows, pigeons, and other birds, and the virus was increasing its ability to infect mammals as well. From this point on, avian flu experts increasingly referred to containment as a strategy that can delay, but not ultimately prevent, a future avian flu pandemic.
"Since 1997, studies of influenza A (H5N1) indicate that these viruses continue to evolve, with changes in antigenicity and internal gene constellations; an expanded host range in avian species and the ability to infect felids; enhanced pathogenicity in experimentally infected mice and ferrets, in which they cause systemic infections; and increased environmental stability."[60]
The New York Times, in an article on transmission of H5N1 through smuggled birds, reports Wade Hagemeijer of Wetlands International stating, "We believe it is spread by both bird migration and trade, but that trade, particularly illegal trade, is more important".[61]
On September 27, 2007 researchers reported that the H5N1 bird flu virus can also pass through a pregnant woman's placenta to infect the fetus. They also found evidence of what doctors had long suspected—that the virus not only affects the lungs, but also passes throughout the body into the gastrointestinal tract, the brain, liver, and blood cells.[62]
| Country | 2003 | 2004 | 2005 | 2006 | 2007 | 2008 | 2009 | 2010 | 2011 | 2012 | Total | ||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| cases | deaths | cases | deaths | cases | deaths | cases | deaths | cases | deaths | cases | deaths | cases | deaths | cases | deaths | cases | deaths | cases | deaths | cases | deaths | ||||||||||||
| 8 | 5 | 63% | 8 | 5 | 63% | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 1 | 0 | 0% | 2 | 0 | 0% | 3 | 0 | 0% | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 4 | 4 | 100% | 2 | 2 | 100% | 1 | 1 | 100% | 1 | 0 | 0% | 1 | 0 | 0% | 1 | 1 | 100% | 8 | 8 | 100% | 1 | 1 | 100% | 19 | 17 | 90% | |||||||
| 1 | 1 | 100% | 8 | 5 | 63% | 13 | 8 | 62% | 5 | 3 | 60% | 4 | 4 | 100% | 7 | 4 | 57% | 2 | 1 | 50% | 1 | 1 | 100% | 1 | 1 | 100% | 42 | 28 | 67% | ||||
| 1 | 0 | 0% | 1 | 0 | 0% | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 18 | 10 | 56% | 25 | 9 | 36% | 8 | 4 | 50% | 39 | 4 | 10% | 29 | 13 | 45% | 39 | 15 | 39% | 1 | 0 | 0% | 159 | 55 | 35% | ||||||||||
| 20 | 13 | 65% | 55 | 45 | 82% | 42 | 37 | 88% | 24 | 20 | 83% | 21 | 19 | 90% | 9 | 7 | 78% | 12 | 10 | 83% | 1 | 1 | 100% | 184 | 152 | 83% | |||||||
| 3 | 2 | 67% | 3 | 2 | 67% | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 2 | 2 | 100% | 2 | 2 | 100% | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 1 | 0 | 0% | 1 | 0 | 0% | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 1 | 1 | 100% | 1 | 1 | 100% | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 3 | 1 | 33% | 3 | 1 | 33% | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 17 | 12 | 71% | 5 | 2 | 40% | 3 | 3 | 100% | 25 | 17 | 68% | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| 12 | 4 | 33% | 12 | 4 | 33% | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 3 | 3 | 100% | 29 | 20 | 69% | 61 | 19 | 31% | 8 | 5 | 63% | 6 | 5 | 83% | 5 | 5 | 100% | 7 | 2 | 29% | 1 | 1 | 100% | 120 | 60 | 50% | |||||||
| Total | 4 | 4 | 100% | 46 | 32 | 70% | 98 | 43 | 44% | 115 | 79 | 69% | 88 | 59 | 67% | 44 | 33 | 75% | 73 | 32 | 44% | 48 | 24 | 50% | 62 | 34 | 55% | 5 | 4 | 80% | 583 | 344 | 59% |
[edit] Society and culture
Main article: Social impact of H5N1
H5N1 has had a significant effect on human society, especially the financial, political, social, and personal responses to both actual and predicted deaths in birds, humans, and other animals. Billions of U.S. dollars are being raised and spent to research H5N1 and prepare for a potential avian influenza pandemic. Over ten billion dollars have been spent and over two hundred million birds killed to try to contain H5N1.[12][63][64][65][66][67][68][69][70]People have reacted by buying less chicken causing poultry sales and prices to fall.[71] Many individuals have stockpiled supplies for a possible flu pandemic. International health officials and other experts have pointed out that many unknown questions still hover around the disease.[72]
Dr. David Nabarro, Chief Avian Flu Coordinator for the United Nations, and former Chief of Crisis Response for the World Health Organization has described himself as "quite scared" about H5N1's potential impact on humans. Nabarro has been accused of being alarmist before and on his first day in his role for the United Nations he proclaimed the avian flu could kill 150 million people. In an interview with the International Herald Tribune, Nabarro compares avian flu to AIDS in Africa, warning that underestimations led to inappropriate focus for research and intervention.[73]
[edit] See also
- Antigenic shift
- Influenza research
- Fujian flu
- H5N1 clinical trials
- International Conference on Emerging Infectious Diseases
- National Influenza Centers
- Swine influenza
- Zoonosis
[edit] References
- ^ International Committee on Taxonomy of Viruses (2002). "46.0.1. Influenzavirus A". http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/ICTVdb/ICTVdB/46010000.htm. Retrieved 2006-04-17.
- ^ a b Li KS, Guan Y, Wang J, Smith GJ, Xu KM, Duan L, Rahardjo AP, Puthavathana P, Buranathai C, Nguyen TD, Estoepangestie AT, Chaisingh A, Auewarakul P, Long HT, Hanh NT, Webby RJ, Poon LL, Chen H, Shortridge KF, Yuen KY, Webster RG, Peiris JS. (2004). "Genesis of a highly pathogenic and potentially pandemic H5N1 influenza virus in eastern Asia". Nature 430 (6996): 209–213. doi:10.1038/nature02746. PMID 15241415.
This was reprinted in 2005:Li KS, Guan Y, Wang J, Smith GJ, Xu KM, Duan L, Rahardjo AP, Puthavathana P, Buranathai C, Nguyen TD, Estoepangestie AT, Chaisingh A, Auewarakul P, Long HT, Hanh NT, Webby RJ, Poon LL, Chen H, Shortridge KF, Yuen KY, Webster RG, Peiris JS. (2005). "Today's Pandemic Threat: Genesis of a Highly Pathogenic and Potentially Pandemic H5N1 Influenza Virus in Eastern Asia,". In Forum on Microbial Threats Board on Global Health: Knobler SL, Mack A, Mahmoud A, Lemon SM. (ed.). The Threat of Pandemic Influenza: Are We Ready? Workshop Summary (2005). Washington DC: The National Academies Press. pp. 116–130. http://darwin.nap.edu/books/0309095042/html/116.html. - ^ "October 11, 2010 FAO Avian Influenza Disease Emergency Situation Update 70" (PDF). http://www.fao.org/docrep/013/ak783e/ak783e00.pdf. Retrieved 2010-12-30.
- ^ a b WHO http://www.who.int/influenza/human_animal_interface/EN_GIP_LatestCumulativeNumberH5N1cases.pdf Cumulative Number of Confirmed Human Cases for Avian Influenza A/(H5N1) Reported to WHO, 2003-2011
- ^ The Fourth ESWI http://www.eswiconference.org Influenza Conference 11-14 September 2011 Malta
- ^ Harmon, Katherine (2011-09-19). "What Will the Next Influenza Pandemic Look Like?". Scientific American. http://www.scientificamerican.com/article.cfm?id=next-influenza-pandemic. Retrieved 2012-01-23.
- ^ Enserink, Martin (2012-01-23). "Scientists Brace for Media Storm Around Controversial Flu Studies". Science. http://news.sciencemag.org/scienceinsider/2011/11/scientists-brace-for-media-storm.html. Retrieved 2012-01-23.
- ^ Ungchusak K, Auewarakul P, Dowell SF, et al. (January 2005). "Probable person-to-person transmission of avian influenza A (H5N1)". N Engl J Med 352 (4): 333–40. doi:10.1056/NEJMoa044021. PMID 15668219.
- ^ Ortiz JR, Katz MA, Mahmoud MN, et al. (December 2007). "Lack of evidence of avian-to-human transmission of avian influenza A (H5N1) virus among poultry workers, Kano, Nigeria, 2006". J Infect Dis 196 (11): 1685–91. doi:10.1086/522158. PMID 18008254.
- ^ a b Webster, R. G. and Walker, E. J. (2003). "The world is teetering on the edge of a pandemic that could kill a large fraction of the human population" ([dead link]). American Scientist 91 (2): 122. doi:10.1511/2003.2.122. http://www.americanscientist.org/template/AssetDetail/assetid/17221?fulltext=true.[dead link]
- ^ United Nations (2005-09-29). "Press Conference by UN System Senior Coordinator for Avian, Human Influenza". UN News and Media Division, Department of Public Information, New York. http://www.un.org/News/briefings/docs/2005/050929_Nabarro.doc.htm. Retrieved 2006-04-17.
- ^ a b Rosenthal, E; Bradsher, K (2006-03-16). "Is Business Ready for a Flu Pandemic?". The New York Times. http://www.nytimes.com/2006/03/16/business/16bird.html?_r=1&oref=slogin. Retrieved 2012-01-23.
- ^ Science and Development Network article Pandemic flu: fighting an enemy that is yet to exist published May 3, 2006.
- ^ a b Robert G. Webster, Ph.D., and Elena A. Govorkova, M.D., Ph.D. (November 23, 2006). "H5N1 Influenza — Continuing Evolution and Spread". NEJM 355 (21): 2174–2177. doi:10.1056/NEJMp068205. PMID 17124014. http://content.nejm.org/cgi/content/full/355/21/2174.
- ^ CDC ARTICLE 1918 Influenza: the Mother of All Pandemics by Jeffery K. Taubenberger published January 2006
- ^ Informaworld article Why is the world so poorly prepared for a pandemic of hypervirulent avian influenza? published December 2006
- ^ Roos, Robert; Lisa Schnirring (February 1, 2007). "HHS ties pandemic mitigation advice to severity". University of Minnesota Center for Infectious Disease Research and Policy (CIDRAP). http://www.cidrap.umn.edu/cidrap/content/influenza/panflu/news/feb0107pandemic.html. Retrieved 2007-02-03.
- ^ Korteweg C, Gu J (May 2008). "Pathology, Molecular Biology, and Pathogenesis of Avian Influenza A (H5N1) Infection in Humans". Am. J. Pathol. 172 (5): 1155–70. doi:10.2353/ajpath.2008.070791. PMC 2329826. PMID 18403604. http://www.pubmedcentral.nih.gov/articlerender.fcgi?tool=pmcentrez&artid=2329826.
- ^ a b Shinya K, Ebina M, Yamada S, Ono M, Kasai N, Kawaoka Y (March 2006). "Avian flu: influenza virus receptors in the human airway". Nature 440 (7083): 435–6. doi:10.1038/440435a. PMID 16554799.
- ^ a b van Riel D, Munster VJ, de Wit E, Rimmelzwaan GF, Fouchier RA, Osterhaus AD, Kuiken T. (2006). "H5N1 Virus Attachment to Lower Respiratory Tract". Science 312 (Epub ahead of print): 399. doi:10.1126/science.1125548. PMID 16556800.
- ^ Leslie Taylor (2006). "Overestimating Avian Flu". Seed Magazine. http://seedmagazine.com/news/2006/01/overestimating_avian_flu.php.
- ^ Anna Thorson, MD, PhD; Max Petzold, PhD; Nguyen Thi Kim Chuc, PhD; Karl Ekdahl, MD, PhD (2006). "Is Exposure to Sick or Dead Poultry Associated With Flulike Illness?". Arch Intern Med 166 (1): 119–123. doi:10.1001/archinte.166.1.119. PMID 16401820. http://archinte.ama-assn.org/cgi/content/full/166/1/119.
- ^ de Jong MD, Bach VC, Phan TQ, Vo MH, Tran TT, Nguyen BH, Beld M, Le TP, Truong HK, Nguyen VV, Tran TH, Do QH, Farrar J. (2005). "Fatal avian influenza A (H5N1) in a child presenting with diarrhea followed by coma". N. Engl. J. Med. 352 (7): 686–691. doi:10.1056/NEJMoa044307. PMID 15716562. http://content.nejm.org/cgi/content/short/352/7/686.
- ^ Chan MC, Cheung CY, Chui WH, Tsao SW, Nicholls JM, Chan YO, Chan RW, Long HT, Poon LL, Guan Y, Peiris JS. (2005). "Proinflammatory cytokine responses induced by influenza A (H5N1) viruses in primary human alveolar and bronchial epithelial cells". Respir. Res. 6 (1): 135. doi:10.1186/1465-9921-6-135. PMC 1318487. PMID 16283933. http://www.pubmedcentral.nih.gov/articlerender.fcgi?tool=pmcentrez&artid=1318487.
- ^ a b Harder, T. C. and Werner, O. (2006). "Avian Influenza". In Kamps, B. S., Hoffman, C. and Preiser, W. (ed.). Influenza Report 2006. Paris, France: Flying Publisher. ISBN 3-924774-51-X. http://www.influenzareport.com/ir/ai.htm. Retrieved 2006-04-18.
- ^ "WHO changes H5N1 strains for pandemic vaccines, raising concern over virus evolution". CIDRAP. August 18, 2006. http://www.cidrap.umn.edu/cidrap/content/influenza/avianflu/news/aug1806vaccines.html.
- ^ "Antigenic and genetic characteristics of H5N1 viruses and candidate H5N1 vaccine viruses developed for potential use as pre-pandemic vaccines" (PDF). WHO. August 18, 2006. http://www.who.int/csr/disease/avian_influenza/guidelines/recommendationvaccine.pdf.
- ^ CDC article Genome Analysis Linking Recent European and African Influenza (H5N1) Viruses EID Journal Home > Volume 13, Number 5–May 2007 Volume 13, Number 5–May 2007
- ^ Payungporn S, Chutinimitkul S, Chaisingh A, Damrongwantanapokin S, Nuansrichay B, Pinyochon W, Amonsin A, Donis RO, Theamboonlers A, Poovorawan T. (2006). "Discrimination between Highly Pathogenic and Low Pathogenic H5 Avian Influenza A Viruses". Emerging Infectious Diseases 12 (4): 700–1. PMID 16715581. http://www.cdc.gov/ncidod/EID/vol12no04/05-1427.htm.
- ^ Parker, Tara (2009-11-05). "Parker-Pope, Tara. November 5, 2009 "The Cat Who Got Swine Flu." ''New York Times.''". Well.blogs.nytimes.com. http://well.blogs.nytimes.com/2009/11/05/the-cat-who-got-swine-flu/. Retrieved 2010-04-05.
- ^ Couch, R. (1996). "Chapter 58. Orthomyxoviruses Multiplication". In Baron, S. (ed.). Medical Microbiology. Galveston, Texas: The University of Texas Medical Branch at Galveston. ISBN 0-9631172-1-1. http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/bv.fcgi?rid=mmed.section.3069.
- ^ "AVIAN INFLUENZA DETECTED IN BRITISH COLUMBIA". CFIA. January 24, 2009. http://www.inspection.gc.ca/english/corpaffr/newcom/2009/20090124e.shtml.
- ^ "AVIAN INFLUENZA Low Pathogenic H5N1 vs. Highly Pathogenic H5N1 - Latest UPDATE". USDA. August 17, 2006. http://www.usda.gov/wps/portal/!ut/p/_s.7_0_A/7_0_1OB?contentidonly=true&contentid=2006/08/0296.xml.
- ^ a b c Kou Z, Lei FM, Yu J, Fan ZJ, Yin ZH, Jia CX, Xiong KJ, Sun YH, Zhang XW, Wu XM, Gao XB, Li TX. (2005). "New Genotype of Avian Influenza H5N1 Viruses Isolated from Tree Sparrows in China". J. Virol. 79 (24): 15460–15466. doi:10.1128/JVI.79.24.15460-15466.2005. PMC 1316012. PMID 16306617. http://www.pubmedcentral.nih.gov/articlerender.fcgi?tool=pmcentrez&artid=1316012.
- ^ a b c The World Health Organization Global Influenza Program Surveillance Network. (2005). "Evolution of H5N1 avian influenza viruses in Asia". Emerging Infectious Diseases 11 (10): 1515–21. PMID 16318689. http://www.cdc.gov/ncidod/EID/vol11no10/05-0644.htm.
Figure 1 shows a diagramatic representation of the genetic relatedness of Asian H5N1 hemagglutinin genes from various isolates of the virus - ^ Gambaryan A, Tuzikov A, Pazynina G, Bovin N, Balish A, Klimov A. (2006). "Fatal Evolution of the receptor binding phenotype of influenza A (H5) viruses". Virology 344 (2): 432–438. doi:10.1016/j.virol.2005.08.035. PMID 16226289.
- ^ Schultz, J. (2005-11-28). "Bird flu vaccine won't precede pandemic". United Press International. Archived from the original on 2006-04-27. http://web.archive.org/web/20060427122447/http://www.upi.com/ConsumerHealthDaily/view.php?StoryID=20051128-054641-9412r. Retrieved 2006-04-18.
- ^ Enserick, M. (2005-08-12). "Avian Influenza:'Pandemic Vaccine' Appears to Protect Only at High Doses". Science. doi:10.1511/2003.2.122. http://www.sciencemag.org/cgi/content/full/309/5737/996b. Retrieved 2006-04-18.
- ^ Walker, K. (2006-01-27). "Two H5N1 human vaccine trials to begin". Science Daily. Archived from the original on 2006-02-14. http://web.archive.org/web/20060214044724/http://www.sciencedaily.com/upi/index.php?feed=Science&article=UPI-1-20060127-15211900-bc-us-fluwrap.xml. Retrieved 2006-04-18.
- ^ Gao W, Soloff AC, Lu X, Montecalvo A, Nguyen DC, Matsuoka Y, Robbins PD, Swayne DE, Donis RO, Katz JM, Barratt-Boyes SM, Gambotto A. (2006). "Protection of Mice and Poultry from Lethal H5N1 Avian Influenza Virus through Adenovirus-Based Immunization". J. Virol. 80 (4): 1959–64. doi:10.1128/JVI.80.4.1959-1964.2006. PMC 1367171. PMID 16439551. http://www.pubmedcentral.nih.gov/articlerender.fcgi?tool=pmcentrez&artid=1367171.
- ^ a b United States Agency for International Development (2006). "Avian Influenza Response: Key Actions to Date". http://www.usaid.gov/our_work/global_health/home/News/news_items/ai_activities.html. Retrieved 2006-04-18.
- ^ United States Department of Health and Human Services (2002). "Pandemicflu.gov Monitoring outbreaks". http://www.pandemicflu.gov/outbreaks/. Retrieved 2006-04-18.
- ^ Medline Plus (2006–01–12). "Oseltamivir (Systemic)". NIH. Archived from the original on 2006-04-25. http://web.archive.org/web/20060425120952/http://www.nlm.nih.gov/medlineplus/druginfo/uspdi/500062.html. Retrieved 2006-04-18.
- ^ Associated Press, "Tamiflu is Set Aside for WHO," The Wall Street Journal, April 20, 2006, page D6.
- ^ Integrated Regional Information Networks (2006-04-02). "Middle East: Interview with WHO experts Hassan al-Bushra and John Jabbour". Alertnet Reuters foundation. Archived from the original on 2006-04-07. http://web.archive.org/web/20060407052900/http://www.alertnet.org/thenews/newsdesk/IRIN/e83d17668fc60eb55518a76c1de858fd.htm. Retrieved 2006-04-18.
- ^ Bernd Sebastian Kamps and Christian Hoffmann. "Zanamivir". Influenza Report. http://www.influenzareport.com/ir/drugs/zanami.htm. Retrieved 2006-10-15.
- ^ "Delayed antiviral plus immunomodulator treatment still reduces mortality in mice infected by high inoculum of influenza A/H5N1 virus". Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences. Jube 10, 2008. http://www.pnas.org/content/105/23/8091.full.pdf+html. Retrieved 2009-08-31.
- ^ "Oseltamivir-resistant H5N1 virus isolated from Vietnamese girl". CIDRAP. October 14, 2005. http://www.cidrap.umn.edu/cidrap/content/influenza/avianflu/news/oct1405resistance.html. Retrieved 2006-10-15.
- ^ "U.N. Says Bird Flu Awareness Increases". NPR. October 12, 2006. Archived from the original on 2007-10-12. http://web.archive.org/web/20071012165207/http://npr.org/templates/story/story.php?storyId=6160868. Retrieved 2006-10-15.
- ^ Collins PJ, Haire LF, Lin YP, Liu J, Russell RJ, Walker PA, Skehel JJ, Martin SR, Hay AJ, Gamblin SJ. (2008). "Crystal structures of oseltamivir-resistant influenza virus neuraminidase mutants". Nature 453 (7199): 1258–61. doi:10.1038/nature06956. PMID 18480754.
- ^ Garcia-Sosa AT, Sild S, Maran U. (2008). "Design of Multi-Binding-Site Inhibitors, Ligand Efficiency, and Consensus Screening of Avian Influenza H5N1 Wild-Type Neuraminidase and of the Oseltamivir-Resistant H274Y Variant". J. Chem. Inf. Model. 48 (10): 2074–2080. doi:10.1021/ci800242z. PMID 18847186.
- ^ Forbes.com (2006–03–22). "Studies Spot Obstacle to Human Transmission of Bird Flu". Archived from the original on May 23, 2006. http://web.archive.org/web/20060523164541/http://www.forbes.com/lifestyle/health/feeds/hscout/2006/03/22/hscout531699.html. Retrieved 2006-04-18.
- ^ Food and Agricultural Organization of the United Nations (2005). "Wild birds and Avian Influenza". http://www.fao.org/ag/againfo/subjects/en/health/diseases-cards/avian_HPAIrisk.html. Retrieved 2006-04-18.
- ^ Brstilo M. (2006–01–19). "Highly Pathogenic Avian Influenza in Croatia Follow-up report No. 4". http://www.oie.int/eng/info/hebdo/AIS_35.HTM#Sec14. Retrieved 2006-04-18.
- ^ European Food Safety Authority (2006–04–04). "Scientific Statement on Migratory birds and their possible role in the spread of highly pathogenic avian influenza" (PDF). Archived from the original on 2006-05-07. http://web.archive.org/web/20060507103516/http://www.efsa.eu.int/science/ahaw/ahaw_opinions/1438/ahaw_ai_statement_19th_plenmeet1.pdf. Retrieved 2006-04-18.
- ^ "Bird flu may be spread indirectly, WHO says". Reuters. Reuters. 2008-01-17. http://www.reuters.com/article/healthNews/idUSN1616209020080117. Retrieved 2009-09-01.
- ^ Sturm-Ramirez KM, Ellis T, Bousfield B, Bissett L, Dyrting K, Rehg JE, Poon L, Guan Y, Peiris M, Webster RG. (2004). "Reemerging H5N1 Influenza Viruses in Hong Kong in 2002 Are Highly Pathogenic to Ducks". J. Virol. 78 (9): 4892–4901. doi:10.1128/JVI.78.9.4892-4901.2004. PMC 387679. PMID 15078970. http://www.pubmedcentral.nih.gov/articlerender.fcgi?tool=pmcentrez&artid=387679.
- ^ World Health Organization (2005–10–28). "H5N1 avian influenza: timeline" (PDF). http://www.who.int/csr/disease/avian_influenza/Timeline_28_10a.pdf. Retrieved 2006-04-18.
- ^ Chen H, Deng G, Li Z, Tian G, Li Y, Jiao P, Zhang L, Liu Z, Webster RG, Yu K. (2004). "The evolution of H5N1 influenza viruses in ducks in southern China". Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A. 101 (28): 10452–10457. doi:10.1073/pnas.0403212101. PMC 478602. PMID 15235128. http://www.pubmedcentral.nih.gov/articlerender.fcgi?tool=pmcentrez&artid=478602.
- ^ Beigel JH, Farrar J, Han AM, Hayden FG, Hyer R, de Jong MD, Lochindarat S, Nguyen TK, Nguyen TH, Tran TH, Nicoll A, Touch S, Yuen KY; Writing Committee of the World Health Organization (WHO) Consultation on Human Influenza A/H5. (2005). "Avian influenza A (H5N1) infection in humans". N. Engl. J. Med. 353 (13): 1374–1385. doi:10.1056/NEJMra052211. PMID 16192482.
- ^ Rosenthal, E. (2006-04-15). "Bird Flu Virus May Be Spread by Smuggling". The New York Times. http://www.nytimes.com/2006/04/15/world/europe/15bird.html?_r=1&th&emc=th&oref=slogin. Retrieved 2006-04-18.
- ^ Pandemic.org.au "H5N1 Transmission Update". Provax. October 1, 2007. http://www.pandemic.org.au/alertDetail.php?id=000100 Pandemic.org.au. Retrieved January 31, 2010.
- ^ State.gov
- ^ Newswire[dead link]
- ^ MSNBC[dead link] US AID
- ^ "BMO Financial Group". .bmo.com. http://www2.bmo.com/news/article/0,1257,contentCode-4922_divId-4_langId-1_navCode-112,00.html. Retrieved 2010-04-05.
- ^ "Council on Foreign Relations". Cfr.org. http://www.cfr.org/pub8198/laurie_garrett_anthony_s_fauci_michael_osterholm_rita_colwell/the_threat_of_global_pandemics.php. Retrieved 2010-04-05.
- ^ Reuters[dead link] article Vietnam to unveil advanced plan to fight bird flu published on April 28, 2006
- ^ Poultry sector suffers despite absence of bird flu[dead link]
- ^ [1]
- ^ India eNews article Pakistani poultry industry demands 10-year tax holiday published May 7, 2006 says "Pakistani poultry farmers have sought a 10-year tax exemption to support their dwindling business after the detection of the H5N1 strain of bird flu triggered a fall in demand and prices, a poultry trader said."
- ^ International Institute for Sustainable Development (IISD) Scientific Seminar on Avian Influenza, the Environment and Migratory Birds on 10-11 April 2006 published 14 April 2006.
- ^ Donald G. McNeil Jr. (March 28, 2006). "The response to bird flu: Too much or not enough? UN expert stands by his dire warnings". International Herald Tribune. http://www.iht.com/articles/2006/03/27/news/worrier.php?page=1.
[edit] External links
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to: H5N1 |
| Wikinews has related news: Avian Flu |
- Influenza Research Database – Database of influenza genomic sequences and related information.
- WHO World Health Organization
- WHO's Avian Flu Facts Sheet for 2006
- Epidemic and Pandemic Alert and Response Guide to WHO's H5N1 pages
- Avian Influenza Resources (updated) - tracks human cases and deaths
- National Influenza Pandemic Plans
- WHO Collaborating Centres and Reference Laboratories Centers, names, locations, and phone numbers
- FAO Avian Influenza portal Information resources, animations, videos, photos
- FAO Food and Agriculture Organisation - Bi-weekly Avian Influenza Maps - tracks animal cases and deaths
- FAO Bird Flu disease card
- FAO Socio-Economic impact of AI Projects, Information resources
- OIE World Organisation for Animal Health - tracks animal cases and deaths
- Health-EU Portal EU response to Avian Influenza.
- Avian influenza - Q & A's factsheet from European Centre for Disease Prevention and Control
- United Kingdom
- Exotic Animal Disease Generic Contingency Plan — DEFRA generic contingency plan for controlling and eradicating an outbreak of an exotic animal disease. PDF hosted by BBC (a government entity).
- UK Influenza Pandemic Contingency Plan by the National Health Service - a government entity. PDF hosted by BBC
- UK Department of Health
- United States
- Center for Infectious Disease Research and Policy Avian Influenza (Bird Flu): Implications for Human Disease - An overview of Avian Influenza
- PandemicFlu.Gov U.S. Government's avian flu information site
- USAID U.S. Agency for International Development - Avian Influenza Response
- CDC, Centers for Disease Control and Prevention - responsible agency for avian influenza in humans in US - Facts About Avian Influenza (Bird Flu) and Avian Influenza A (H5N1) Virus
- USGS - NWHC National Wildlife Health Center - responsible agency for avian influenza in animals in US
- Wildlife Disease Information Node A part of the National Biological Information Infrastructure and partner of the NWHC, this agency collects and distributes news and information about wildlife diseases such as avian influenza and coordinates collaborative information sharing efforts.
- HHS U.S. Department of Health & Human Services - Pandemic Influenza Plan
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||




0 件のコメント:
コメントを投稿